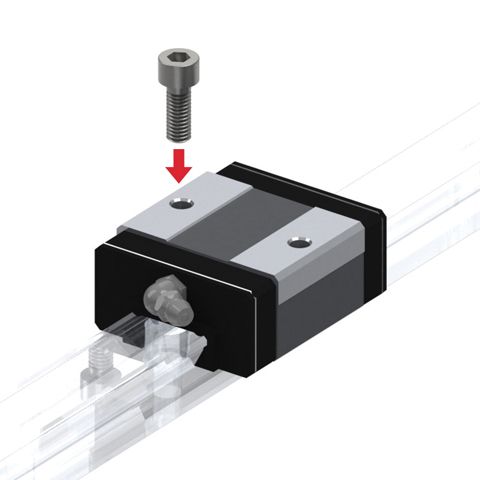
Linear Motion Guides
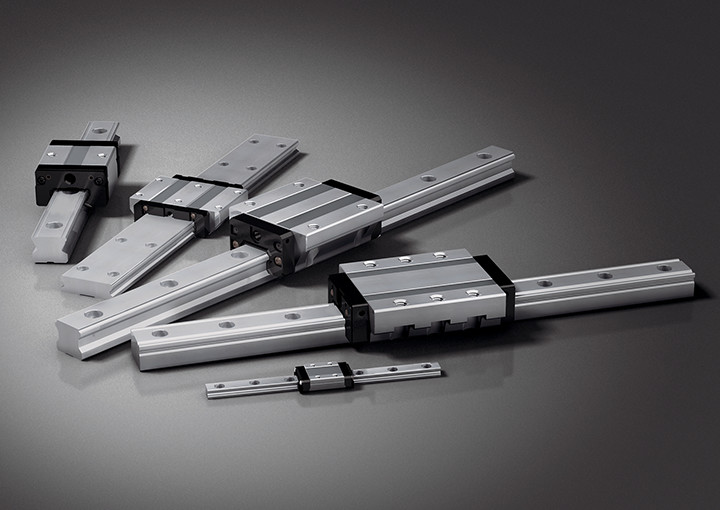

Global Standard Caged Ball LM Guide (SHS)
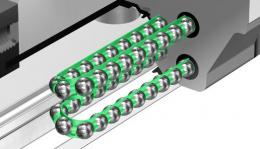
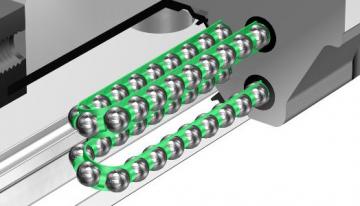
Each row of balls is placed at a contact angle of 45 degree so that the rated loads applied to the LM block are uniform in the four directions (radial, reverse radial and lateral directions), enabling the LM Guide to be used in all orientations. Use of the ball cage eliminates friction between balls and increases grease retention, thus to achieve low noise, high speed and long-term maintenance-free operation.
Global Standard Caged Ball LM Guide (SHS)
Diagram - Global Standard Caged Ball LM Guide (SHS)
Global Standard Caged Ball LM Guide (SHS-M) – Stainless Steel
Stainless steel variant of SHS. Each row of balls is placed at a contact angle of 45 degree so that the rated loads applied to the LM block are uniform in the four directions (radial, reverse radial and lateral directions), enabling the LM Guide to be used in all orientations. Use of the ball cage eliminates friction between balls and increases grease retention, thus to achieve low noise, high speed and long-term maintenance-free operation.
Global Standard Caged Ball LM Guide (SHS-M) – Stainless Steel

Diagram - Global Standard Caged Ball LM Guide (SHS-M) – Stainless Steel
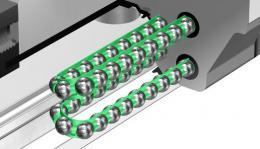
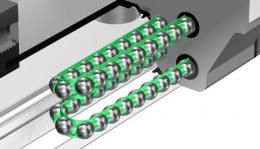
Radial Type Caged Ball LM Guide (SSR)
The compact design with a low sectional height and the ball contact structure at 90° in the radial direction make this model an optimal model for horizontal guide units. Use of the ball cage eliminates friction between balls and increases grease retention, thus to achieve low noise, high speed and long-term maintenance-free operation.
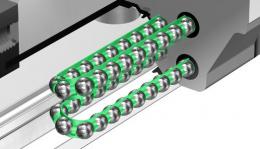
Radial Type Caged Ball LM Guide (SSR)
Diagram - Radial Type Caged Ball LM Guide (SSR)
Radial Type Caged Ball LM Guide (SSR) - Stainless Steel
Radial Type Caged Ball LM Guide (SSR) - Stainless Steel

Diagram - Radial Type Caged Ball LM Guide (SSR) - Stainless Steel
Wide, Low Gravity Center Caged Ball LM Guide (SHW)
Model SHW, which has a wide LM rail and a low center of gravity, is optimal for locations requiring space saving and large Mc moment rigidity. Use of the ball cage eliminates friction between balls and increases grease retention, thus to achieve low noise, high speed and long-term maintenance-free operation.
Wide, Low Gravity Center Caged Ball LM Guide (SHW)
Diagram - Wide, Low Gravity Center Caged Ball LM Guide (SHW)
Miniature Caged Ball LM Guide (SRS)
Caged Ball LM Guide model SRS has a structure where two raceways are incorporated into the compact body, enabling the model to receive loads in all directions, and to be used in locations where a moment is applied with a single rail. In addition, use of ball cages eliminates friction between balls, thus achieving high speed, low noise, acceptable running sound, long service life, and long-term maintenance-free operation.
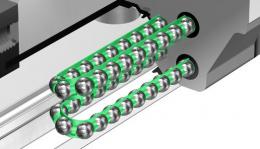
Miniature Caged Ball LM Guide (SRS)
Diagram - Miniature Caged Ball LM Guide (SRS)
Global Standard LM Guide (HSR)
Each row of balls is placed at a contact angle of 45 degree so that the rated loads applied to the LM block are uniform in the four directions (radial, reverse radial and lateral directions), enabling the LM Guide to be used in all orientations and in extensive applications.
Diagram - Global Standard LM Guide (HSR)
Global Standard LM Guide (HSR) - Stainless Steel
Diagram - Global Standard LM Guide (HSR) - Stainless Steel
Global Standard Roller Guide (HRX)
4-Way Equal Load Roller Guide suitable for ultra-high rigidity and ultra heavy loads. The HRX uses rollers as a rolling element for higher rigidity. Each row of rollers is arranged at a contact angle of 45° so that the LM block has equal load ratings in all directions (radial, reverse radial, and horizontal directions), ensuring high rigidity in all directions.

Global Standard Roller Guide (HRX)
Diagram - Global Standard Roller Guide (HRX)
Radial Type LM Guide (SR)
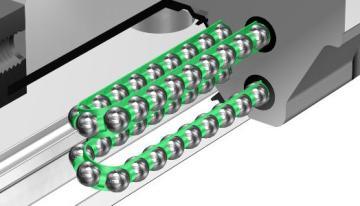
Radial Type LM Guide (SR)
Diagram - Radial Type LM Guide (SR)
Radial Type LM Guide (SR) - Stainless Steel
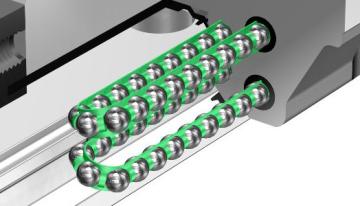
Radial Type LM Guide (SR) - Stainless Steel
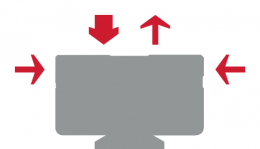
Diagram - Radial Type LM Guide (SR) - Stainless Steel
Wide, Low Gravity Center LM Guide (HRW)
Model HRW, which has a wide LM rail and a low center of gravity, is optimal for locations requiring space saving and large Mc moment rigidity.
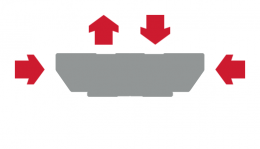
Diagram - Wide, Low Gravity Center LM Guide (HRW)
Miniature LM Guide
THK's miniature LM Guide series with with uncaged, full-complement bearings. These models are capable of receiving loads in all directions, and a single-rail guide can adequately operate under a small moment load.
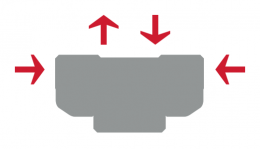
Diagram - Miniature LM Guide
Separate Type (GSR)
Since model GSR has a low center of gravity structure with a low overall height, the machine can be downsized.* Model GSR cannot be used in single-axis applications.

Diagram - Separate Type (GSR)
Separate Type (HR)
Model HR is easier to adjust a clearance and highly capable of absorbing a mounting error. When the two rails are mounted in parallel, each row of balls is placed at a contact angle of 45 degree so that the rated loads applied to the LM block are uniform in the four directions (radial, reverse radial and lateral directions).
Diagram - Separate Type (HR)